Data Model Overview
The enmeshed data model can be divided into three parts:
- Transport types
- Local types
- Content types
The following diagram gives you an overview of all the existing types and how they are connected to each other. The subsequent chapters describe these types in more detail.
(note that you can click on each type in order to navigate to the paragraph with the corresponding description)
At a first glance the amount of types is overwhelming. But in the following chapters all of them are explained in detail.
Transport Types
Transport types like RelationshipTemplate, Token or File are types that are “exchanged” between Identities via the Backbone.
They are created and updated by the Transport Layer.
In most cases they have a content property, which contains the actual payload that should be transferred between the Identities.
This payload is being encrypted when it is sent to the Backbone, and decrypted by the other Identity when it is received.
The following sections describe the different Transport types and their properties.
Note that the properties of the types are the ones that exist locally (aka on the Connector/in the App). The Backbone does not necessarily know about them. The properties that only exist locally are marked accordingly in the tables below. Further there are properties that are confidential and are therefore encrypted before sent to the Backbone, in order to enable end-to-end encryption. Both kinds of these properties are marked accordingly in the “Remarks” column of the property tables below.
Token
Tokens can be used to save arbitrary structured data on the Backbone, which is encrypted with a random symmetric key. You can then pass the ID of the Token, together with the random key, to another Identity, which can then retrieve the token and decrypt it, e.g. inside of a QR code, which you send to the recipient via letter. Tokens can be handy in a lot of scenarios, for example:
- You want to share secret information with someone you don’t have a Relationship with.
- The enmeshed App currently uses a Token to save a Backup of the Identity.
The Token’s
reference.urlis then encoded in a QR code, which the user can print out and scan later in order to restore the Identity on a new device.
A Token has the following properties:
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each Token starts with the letters "TOK". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| isOwn | boolean |
true if the Token was created by yourself, false if it was created by someone else. |
saved only locally |
| createdBy | string |
The address of the Identity that created the Token. |
|
| createdByDevice | string |
The ID of the Device that created the Token. You can use this information to track back who exactly did what. | |
| content | unknown |
The content of the Token. You can add whatever you want here. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the Token was created. | |
| expiresAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the Token expires on the Backbone. An expired Token cannot be fetched from the Backbone anymore. However, the stored version of the Token on Connector and App will still be accessible. | |
| forIdentity | string | undefined |
Can be set to an enmeshed address. If set, then only the Identity with that address can retrieve the Token from the Backbone. |
|
| passwordProtection | PasswordProtection | undefined |
Information about whether or not the Token is protected by a password or pin. | |
| reference | ObjectReference |
The reference of the Token. | saved only locally |
| isEphemeral | boolean |
If set to true the Token will not be persisted in the database and only displayed once. You will not be able to fetch this Token unless you remember its reference. |
PasswordProtection
A Token or RelationshipTemplate can be protected by a password to ensure that it is protected from unauthorized access.
In order for a peer to establish a Relationship to the creator of a password protected RelationshipTemplate, it must enter the correct password when loading the RelationshipTemplate.
Similarly, in order for an Identity to load a Token that is password protected, it must enter the correct password.
Information about the password protection of a Token or a RelationshipTemplate is recorded within its optional passwordProtection property.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| password | string |
The password of the Token or the RelationshipTemplate. | |
| passwordIsPin | true | undefined |
If the password consists of 4 to 16 digits, the value of the passwordIsPin property can be set to true. In this case, the password is interpreted as a pin and a corresponding input field is displayed in the App when the pin needs to be entered. However, if the value is undefined, a regular input field for entering the password is displayed regardless of whether the password could also be interpreted as a pin. |
ObjectReference
The data objects Token, RelationshipTemplate and File have a reference.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| truncated | string |
The Base64 encoded truncated reference of this object, which actually consists of all information to get and decrypt it. | |
| url | string |
The object reference as a URL, consisting of all information to get and decrypt it. In addition, this URL is valid for browsers and therefore it is possible to show a help page if it is tried to access the object when the App is not installed. |
RelationshipTemplate
A RelationshipTemplate serves two purposes:
- It represents the permission to establish a Relationship. When initiating a Relationship, the ID of a valid RelationshipTemplate must be attached. Otherwise the Backbone blocks the Relationship. And since the IDs are randomly generated, you can only obtain such an ID from the RelationshipTemplate’s owner.
- It can contain data which is of interest for the one who uses the RelationshipTemplate.
The enmeshed App for example expects a RelationshipTemplate content which contains a
Requestwhich contains e.g. Attributes about the creator of the RelationshipTemplate as well as queries for Attributes that the RelationshipTemplate creator wants to receive together with the Relationship.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each RelationshipTemplate starts with the letters "RLT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| isOwn | boolean |
true if the RelationshipTemplate was created by yourself, false if it was created by someone else. |
saved only locally |
| createdBy | string |
The address of the Identity that created the RelationshipTemplate. |
|
| createdByDevice | string |
The ID of the Device that created the RelationshipTemplate. You can use this information to track back who exactly did what. | |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the RelationshipTemplate was created. | |
| content | RelationshipTemplateContent | ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent |
The content of the RelationshipTemplate. If it is intended for a User of the enmeshed App, RelationshipTemplateContent has to be used. Otherwise, an ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent can also be used, which can be filled with anything and serves as a fallback if the RelationshipTemplateContent is not sufficient. |
|
| expiresAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the RelationshipTemplate expires on the Backbone. An expired RelationshipTemplate cannot be fetched from the Backbone anymore. However, the stored version of the RelationshipTemplate on Connector and App will still be accessible. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| maxNumberOfAllocations | number | undefined |
Can be set to limit the number of allocations of this RelationshipTemplate. A RelationshipTemplate is allocated by another Identity when it is first retrieved by it from the Backbone. After this value is reached, the Backbone rejects each request of any new Identity that wants to retrieve it. Identities that already allocated it will still be able to retrieve it. | |
| forIdentity | string | undefined |
Can be set to an enmeshed address. If set, then only the Identity with that address can retrieve the RelationshipTemplate from the Backbone. |
|
| passwordProtection | PasswordProtection | undefined |
Information about whether or not the RelationshipTemplate is protected by a password or pin. | |
| reference | ObjectReference |
The reference of the RelationshipTemplate. | saved only locally |
Relationship
A Relationship between two Identities is the prerequisite for them to exchange Messages. If there is no Relationship, the Backbone blocks all Messages that are tried to be sent. This ensures that you only receive Messages from Identities you know, so you are protected from any harmful Messages like spam or phishing mails.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each Relationship starts with the letters "REL". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| templateId | string |
The ID of the RelationshipTemplate that was used to establish this Relationship. | |
| status | "Pending" | "Active" | "Rejected" | "Revoked" | "Terminated" | "DeletionProposed" |
The status of this Relationship.
|
|
| creationContent | RelationshipCreationContent | ArbitraryRelationshipCreationContent |
The content sent along when the Relationship is initiated. If the template contains a RelationshipTemplateContent, RelationshipCreationContent has to be used. Otherwise, an ArbitraryRelationshipCreationContent is used, which can be filled with anything. |
will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity with which you have this Relationship. |
|
| peerIdentity | Identity |
The Identity with which you have this Relationship. | |
| peerDeletionInfo | PeerDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the Identity with which you have this Relationship is to be deleted or was deleted, as well as the point in time of that deletion. | |
| auditLog | RelationshipAuditLogEntry[] |
A log of Relationship operations like creating or accepting a pending Relationship. |
PeerDeletionInfo
The initiation of the deletion of an Identity as well as the actual deletion of an Identity logically have side effects for the peers of their Relationships.
Whether the Identity with which you have a Relationship is to be deleted or has already been deleted is therefore recorded in the peerDeletionInfo property of the Relationship by a data object of type PeerDeletionInfo.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| deletionStatus | "ToBeDeleted" | "Deleted" |
A status that describes whether the Identity with which you have the Relationship is to be deleted or has already been deleted. | |
| deletionDate | string |
The point in time the Identity with which you have the Relationship is to be deleted or was deleted. |
RelationshipAuditLogEntry
The audit log records Relationship operations starting with the creation of the Relationship in status Pending.
For the full list of tracked operations see the property reason.
Each entry of the log is timestamped and states who executed the operation.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the Relationship operation was executed. | |
| createdBy | string |
The address of the Identity that executed the Relationship operation. |
|
| createdByDevice | string |
The ID of the Device that executed the Relationship operation. You can use this information to track back who exactly did it. | |
| reason | "Creation" | "AcceptanceOfCreation" | "RejectionOfCreation" | "RevocationOfCreation" | "Termination" | "ReactivationRequested" | "AcceptanceOfReactivation" | "RejectionOfReactivation" | "RevocationOfReactivation" | "Decomposition" | "DecompositionDueToIdentityDeletion" |
The type of the Relationship operation.
|
|
| oldStatus | "Pending" | "Active" | "Terminated" | undefined |
The status of the Relationship before the operation, it’s undefined if the operation is the Relationship’s creation. |
|
| newStatus | "Pending" | "Active" | "Rejected" | "Revoked" | "Terminated" | "DeletionProposed" |
The status of the Relationship after the operation. |
Message
A Message is a piece of data that can be sent to one or more recipients.
The sender is completely free in what the content of the Message looks like.
Though in order to enable a normalized communication, enmeshed defines some content structures for Messages, and in the future there will be more of those.
Consider that the enmeshed App only supports Messages with such a normalized content.
Currently there are:
You can read more details about each of these in the corresponding sections of the “Content Types” chapter.
But if you are communicating with another Connector, you can use the ArbitraryMessageContent to send any structure that fits your needs.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each Message starts with the letters "MSG". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| content | Mail | Request | ResponseWrapper | Notification | ArbitraryMessageContent |
The content of the Message. You can add whatever you want here by using ArbitraryMessageContent. However, if it is intended for a User of the enmeshed App, use either Mail, Request, ResponseWrapper or Notification. |
will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| createdBy | string |
The address of the Identity that created the Message. |
|
| createdByDevice | string |
The ID of the Device that created the Message. You can use this information to track back who exactly did what. | |
| recipients | Recipient[] |
An array of recipients of this Message without duplicates. | |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the Message was created. | |
| attachments | string[] |
An array of File IDs without duplicates you want to attach to your Message. You receive the File ID after you uploaded a file to the Backbone. By attaching a File to a Message, you share the secret key used to encrypt/decrypt the File, which cannot be undone. | |
| isOwn | boolean |
Indicates whether you are the sender (true) or recipient (false) of the Message. |
|
| wasReadAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the Message was firstly read. If a Message is marked as unread, this will be undefined. If a Message is read again, after having marked it as unread, the timestamp is updated. However, if a Message marked as read is read again, it won’t be updated. |
Recipient
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| address | string |
The address of the recipient of the Message. | |
| relationshipId | string |
The ID of the Relationship between the recipient and the sender of the Message. | saved only locally |
| receivedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp that describes when the recipient retrieved the Message from the Backbone. undefined when the Message wasn’t received yet. Caution: “received” does not mean that it was read, so don’t mix this up with a read receipt. |
|
| receivedByDevice | string | undefined |
The ID of the Device that first retrieved the Message. undefined when the Message wasn’t received yet. This is of no interest for the sender of the Message, but rather for the recipient itself, since they can use it for audit purposes. |
File
The Backbone allows you to upload a file in encrypted form. Its metadata information is stored in a data object of type File. A File further has its content, of course. But since this is not a JSON property, it is not included in the following table. The content of the File can be downloaded separately by executing the Download File use case.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each File starts with the letters "FIL". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the File was created. | |
| createdBy | string |
The address of the Identity that created the File. |
|
| createdByDevice | string |
The ID of the Device that created the File. You can use this information to track back who exactly did what. | |
| expiresAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the File expires on the Backbone. An expired File cannot be fetched from the Backbone anymore. However, the stored version of the File on Connector and App will still be accessible. | |
| filename | string |
The name of the file as it was on the device that uploaded it. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| filesize | number |
The size of the plaintext file in bytes. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| tags | string[] | undefined |
To specify additional information. A tag is valid if it is contained in the AttributeTagCollection for the IdentityAttribute value.@type IdentityFileReference and starts with the prefix bkb: or if it starts with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$. This validation is needed as an associated IdentityAttribute with IdentityFileReference as value.@type will have these tags as well if it is created for the File during transferring its ownership to a peer. |
will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| mimetype | string |
The mimetype of the file. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| title | string |
A human readable title of the file, which can be defined when uploading the File. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| description | string | undefined |
A human readable description of the file, which can be defined when uploading the File. | will be encrypted before sent to the Backbone |
| isOwn | boolean |
true if the File was created by yourself, false if it was created by someone else. |
saved only locally |
| reference | ObjectReference |
The reference of the File. | saved only locally |
| ownershipToken | string | undefined |
If the ownership of the File should be transferred to another Identity, the ownershipToken must be specified in the according TransferFileOwnershipRequestItem. This property is only set for the owner of the File. | |
| ownershipIsLocked | true | undefined |
If an Identity tries to claim the ownership of the File with an incorrect ownershipToken, the File will be locked for further claims, which this property indicates. In order to unlock it, it is necessary to regenerate the ownershipToken. This property can only be set for the owner of the File. |
Identity
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| address | string |
The unique address of the Identity. | |
| publicKey | string |
The public key of the Identity. |
IdentityDeletionProcess
If you want to delete your Identity, the actual deletion of all data associated with that Identity will only take place after a certain grace period has ended.
Up until then, the data about the deletion process is stored in an object called IdentityDeletionProcess.
It is possible to cancel an IdentityDeletionProcess that hasn’t reached the end of its grace period, yet.
Since cancelled IdentityDeletionProcesses are stored, you can reach a situation in which there are multiple IdentityDeletionProcesses associated with the same Identity.
Note, however, that at all times there can only be at most one active IdentityDeletionProcess, i.e. with "Active" as status, per Identity.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each IdentityDeletionProcess starts with the letters "IDP". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| status | "Active" | "Cancelled" |
The status of the IdentityDeletionProcess.
|
|
| createdAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp that describes when the IdentityDeletionProcess was created. | |
| createdByDevice | string | undefined |
The ID of the Device that created the IdentityDeletionProcess. You can use this information to track back who exactly did what. | |
| gracePeriodEndsAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp that describes when the Identity will be permanently deleted. Up until this moment, it is possible to cancel the IdentityDeletionProcess. | |
| cancelledAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp that describes when the IdentityDeletionProcess was cancelled. | |
| cancelledByDevice | string | undefined |
The ID of the Device that cancelled the IdentityDeletionProcess. |
Local Types
In addition to the types that are shared between Identities via the Backbone, there are certain types that only exist within one Identity. These types usually contain metadata about Content types that should not be transferred to other Identities. They are created and updated by the Consumption Layer.
Currently there are three main Local types:
- LocalRequest
- LocalNotification
- LocalAttribute
Each of them further describes some sub types.
This chapter explains all of those types, together with their properties.
LocalRequest
A LocalRequest contains the local metadata for a Request.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalRequest starts with the letters "REQ". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| isOwn | boolean |
true if you sent the Request, false if you received it. |
| peer | string |
The Identity that sent you the corresponding Request/that you sent the Request to. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalRequest was created. |
| status | LocalRequestStatus |
The current status of the Request. See below for a list of all possible values. |
| content | Request |
The actual Content object this LocalRequest defines the metadata for. |
| source | LocalRequestSource | undefined |
Information about the Transport object with which the Request came in/was sent. This property is undefined if the Request is not sent yet. |
| response | LocalResponse | undefined |
Metadata + Content object of the response. If there is no response yet, this property is undefined. |
| wasAutomaticallyDecided | true | undefined |
Indicates whether the Request was decided automatically by the Decider Module. This will only be set for the recipient of the Request. |
LocalRequestStatus
Depending on whether it is an incoming or an outgoing Request, there can be different statuses. The following state diagram shows which status exists in both cases and when there are transitions from one state to another:
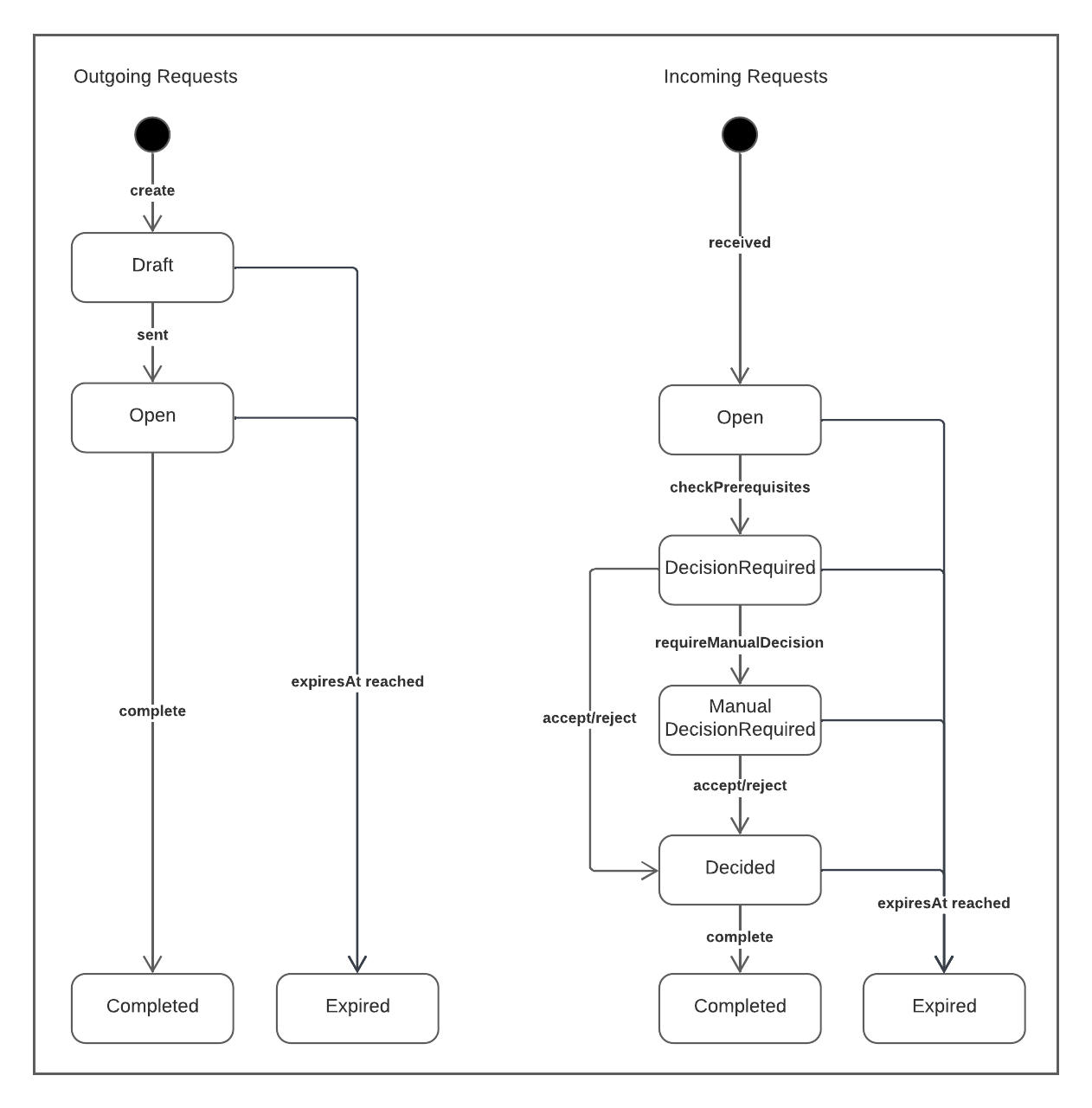
- Draft
- This status only exists for outgoing Requests. It means that the LocalRequest was created, but not yet sent.
- Open
- In case of an outgoing Request,
Openmeans that the Request was sent. The transition toOpenhappens automatically when you send the Request with a Message. - In case of an incoming Request,
Openmeans that the LocalRequest was received. - DecisionRequired
- After the prerequisites of the Request and all of its RequestItems were checked, a decision can be made.
At first, the Decider Module tries to make an automatic decision.
It therefore checks all LocalRequests in status
DecisionRequired. - ManualDecisionRequired
- If the Decider Module cannot make a decision, it moves the LocalRequest to
ManualDecisionRequired. When the LocalRequest is in this status, it’s the User’s turn to decide whether they want to accept or reject the Request. - Decided
- When the User or the Decider Module accepts or rejects the Request, the Response and ResponseItems are generated based on the passed parameters.
This Response is saved in the
responseproperty of theLocalRequest, but not yet sent. - Completed
- In case of an incoming Request, the Runtime Module listens to an Event saying that a Request moved to status
Decided. It then checks on which way the Request was received (Message/RelationshipTemplate) and sends the Response on the corresponding way (by sending a Message or creating a Relationship). After the Response was successfully sent, it moves the LocalRequest toCompleted. - In case of an outgoing Request, the Runtime Module listens to the
MessageReceivedEventand checks the content of the sent Message for a Response. If there is one, it moves the corresponding LocalRequest toCompleted. - Expired
- When the timestamp in
expiresAtof a Request is reached, the Request automatically moves to the statusExpired.
LocalRequestSource
With the information in this type you can clearly identify the Transport object the Request was sent/received in. Currently there are only two possibilities: Message and RelationshipTemplate.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | "Message" | "RelationshipTemplate" |
The type of Transport object the Request was sent/received in. |
| reference | string |
The ID of the Transport object the Request was sent/received in. |
LocalResponse
When a LocalRequest is decided/received, a Local Response is generated, which contains the Response, together with some metadata.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalResponse was created. |
| content | Response |
The actual Content object this Local Response defines the metadata for. |
| source | LocalResponseSource | undefined |
Information about the Transport object with which the Response came in/was sent. This property is undefined if the Response is not sent/received yet. |
LocalResponseSource
With the information in this type you can clearly identify the Transport object the Response was sent/received in. Currently there are only two possibilities: Message and Relationship.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | "Message" | "Relationship" |
The type of Transport object the Response was sent/received in. |
| reference | string |
The ID of the Transport object the Response was sent/received in. |
LocalNotification
A LocalNotification contains the local metadata for a Notification.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalNotification starts with the letters "NOT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| isOwn | boolean |
true if you sent the Notification, false if you received it. |
| peer | string |
The Identity that sent you the corresponding Notification/that you sent the Notification to. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalNotification was created. |
| status | LocalNotificationStatus |
The current status of the Notification. See below for a list of all possible values. |
| content | Notification |
The actual Content object this LocalNotification defines the metadata for. |
| source | LocalNotificationSource |
Information about the Transport object with which the Notification came in/was sent. |
| receivedByDevice | string | undefined |
The ID of the device that received the Notification. For reasons of consistence, the Notification can only be processed by this device. |
LocalNotificationStatus
Depending on whether it is an incoming or an outgoing Notification, there can be different statuses.
- Sent
- This is the only valid status on sender side.
If a Notification is sent and, therefore, a LocalNotification is created, its status will be set to
Sent. - Open
- Receiving a Notification, a LocalNotification is created with status
Open. - Completed
- After receiving a Notification, its items will be processed internally.
If all processes finish successfully, the status of the LocalNotification will be set to
Completed. - Error
- If an error occurs while processing the items of a received Notification, the status of the LocalNotification will be set to
Error.
LocalNotificationSource
With the information in this type you can clearly identify the Transport object the Notification was sent/received in. Currently, the only possibility for transmitting Notifications are Messages.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | “Message” | The type of Transport object the Notification was sent/received in. So far, Notifications can only be transmitted via Messages. |
| reference | string |
The id of the Transport object the Notification was sent/received in. |
LocalAttribute
A LocalAttribute stores the local metadata for an Attribute.
This is contained within the content property of the LocalAttribute.
The Attribute can be an IdentityAttribute or a RelationshipAttribute.
To represent who the owner of an Attribute is and who shared or received an Attribute, there are different subtypes of LocalAttributes.
In the Attribute introduction, more details on the terminology related to LocalAttributes can be found.
OwnIdentityAttribute
If an Identity creates an IdentityAttribute for itself, it is referred to as an OwnIdentityAttribute.
The Identity can share an IdentityAttribute of itself with another Identity by exchanging it using a suitable Request.
In that case, AttributeForwardingDetails are created, with their attributeId property set to the id of the OwnIdentityAttribute to represent their association.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalAttribute starts with the letters "ATT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| content | IdentityAttribute |
The actual Content object this LocalAttribute defines the metadata for. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalAttribute was created. |
| succeeds | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing predecessor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. The value of its succeeds property is then the id of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no predecessor, its succeeds property is undefined. |
| succeededBy | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing successor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. Its id is then the value of the succeededBy property of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no successor, its succeededBy property is undefined. |
| wasViewedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the LocalAttribute was firstly viewed. |
| isDefault | true | undefined |
States whether the LocalAttribute is the default OwnIdentityAttribute for its Attribute value type. If setting default OwnIdentityAttributes is enabled, for every IdentityAttribute value type exactly one OwnIdentityAttribute will have isDefault set, given that at least one OwnIdentityAttribute of that value type exists. This property is only used for the UI of the App, e.g. to mark the Attribute that should be displayed firstly if multiple Attributes of the same value type exist. Thus, for a Connector it will always be undefined. |
PeerIdentityAttribute
If an Identity shares an OwnIdentityAttribute with a peer, a PeerIdentityAttribute is created for the peer. An IdentityAttribute received from another Identity cannot be shared further.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalAttribute starts with the letters "ATT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| content | IdentityAttribute |
The actual Content object this LocalAttribute defines the metadata for. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalAttribute was created. |
| succeeds | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing predecessor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. The value of its succeeds property is then the id of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no predecessor, its succeeds property is undefined. |
| succeededBy | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing successor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. Its id is then the value of the succeededBy property of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no successor, its succeededBy property is undefined. |
| wasViewedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the LocalAttribute was firstly viewed. |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity the LocalAttribute was received from. |
| sourceReference | string |
The id of the LocalRequest or LocalNotification the LocalAttribute was received in. |
| deletionInfo | ReceivedAttributeDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the PeerIdentityAttribute is to be deleted or the OwnIdentityAttribute was deleted by the emitter, as well as the point in time of that deletion. |
ReceivedAttributeDeletionInfo
The ReceivedAttributeDeletionInfo holds information about the deletion status of the Attribute, as well as the point in time of that deletion.
If the Attribute’s emitter requests the deletion of a shared Attribute via a DeleteAttributeRequestItem from the recipient, the recipient can accept or reject it.
If the recipient accepts the DeleteAttributeRequestItem, the deletionStatus of the recipient’s Attribute will be set to "ToBeDeleted" and its deletionDate will be set to the deletionDate the recipient sent with their DeleteAttributeAcceptResponseItem.
Once the recipient’s Attribute is deleted by the recipient, a ForwardedAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem or a PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem is sent to the emitter, enabling it to update its corresponding EmittedAttributeDeletionInfo.
If the emitter deletes their emitted Attribute, before the recipient deleted their Attribute, either an OwnAttributeDeletedByOwnerNotificationItem or, in a special case, a PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem is sent to the recipient.
If the deletionInfo of the recipient was undefined before, the deletionStatus will be set to "DeletedByEmitter" with the time of processing the NotificationItem as deletionDate.
However, if the deletionInfo was defined before with "ToBeDeleted" as deletionStatus, it will remain unchanged, such that the recipient will be able to delete their Attribute as planned.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| deletionStatus | "ToBeDeleted" | "DeletedByEmitter" |
The deletion status of the Attribute. |
| deletionDate | string |
The point in time
|
OwnRelationshipAttribute
RelationshipAttributes always exist in the context of a Relationship.
For this reason, it is not possible for an Identity to have an unshared RelationshipAttribute.
The creation of a RelationshipAttribute corresponds to the creation of an OwnRelationshipAttribute for its owner and a PeerRelationshipAttribute for the peer with whom the owner has established the Relationship in whose context the RelationshipAttribute is to exist.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalAttribute starts with the letters "ATT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| content | RelationshipAttribute |
The actual Content object this LocalAttribute defines the metadata for. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalAttribute was created. |
| succeeds | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing predecessor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. The value of its succeeds property is then the id of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no predecessor, its succeeds property is undefined. |
| succeededBy | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing successor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. Its id is then the value of the succeededBy property of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no successor, its succeededBy property is undefined. |
| wasViewedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the LocalAttribute was firstly viewed. |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity the LocalAttribute was shared with. |
| sourceReference | string |
The id of the LocalRequest or LocalNotification the LocalAttribute was sent with. |
| deletionInfo | EmittedAttributeDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the PeerRelationshipAttribute of the peer of the Relationship is to be deleted or was deleted by the peer, as well as the point in time of that deletion. |
EmittedAttributeDeletionInfo
The EmittedAttributeDeletionInfo holds information about the deletion status of the Attribute, as well as the point in time of that deletion.
If the Attribute’s emitter requests the deletion of a shared Attribute via a DeleteAttributeRequestItem from the recipient, the emitted Attribute will get "DeletionRequestSent" as deletionStatus and the time of sending the Request as deletionDate.
If the recipient rejects the DeleteAttributeRequestItem, the emitted Attribute will get "DeletionRequestRejected" as deletionStatus and the time of receiving the RejectResponseItem as deletionDate.
If the recipient accepts, however, the deletionStatus of the emitter’s Attribute will change to "ToBeDeletedByRecipient" and the deletionDate will be the same as the deletionDate of the received DeleteAttributeAcceptResponseItem.
Either a ForwardedAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem or a PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem is sent to the emitter, once the recipient’s Attribute is deleted.
Finally, the deletionStatus of the emitted Attribute is set to "DeletedByRecipient" with the time of processing the NotificationItem as deletionDate.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| deletionStatus | "DeletionRequestSent" | "DeletionRequestRejected" | "ToBeDeletedByRecipient" | "DeletedByRecipient" |
The deletion status of the Attribute. |
| deletionDate | string |
The point in time
|
PeerRelationshipAttribute
RelationshipAttributes always exist in the context of a Relationship.
For this reason, it is not possible for an Identity to have an unshared RelationshipAttribute.
The creation of a RelationshipAttribute corresponds to the creation of an OwnRelationshipAttribute for its owner and a PeerRelationshipAttribute for the peer with whom the owner has established the Relationship in whose context the RelationshipAttribute is to exist.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalAttribute starts with the letters "ATT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| content | RelationshipAttribute |
The actual Content object this LocalAttribute defines the metadata for. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalAttribute was created. |
| succeeds | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing predecessor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. The value of its succeeds property is then the id of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no predecessor, its succeeds property is undefined. |
| succeededBy | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing successor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. Its id is then the value of the succeededBy property of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no successor, its succeededBy property is undefined. |
| wasViewedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the LocalAttribute was firstly viewed. |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity the LocalAttribute was received from. |
| sourceReference | string |
The id of the LocalRequest or LocalNotification the LocalAttribute was received in. |
| deletionInfo | ReceivedAttributeDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the PeerRelationshipAttribute is to be deleted or the OwnRelationshipAttribute is deleted by the emitter, as well as the point in time of that deletion. |
ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute
A RelationshipAttribute can be forwarded to a peer which is not involved in the Relationship in which the RelationshipAttribute exists if its confidentiality is not set to "private".
For the Identity which forwards its OwnRelationshipAttribute or PeerRelationshipAttribute to a peer, AttributeForwardingDetails are created, with their attributeId property set to the id of the source RelationshipAttribute to represent their association.
A ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute is created for the Identity which received the forwarded RelationshipAttribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each LocalAttribute starts with the letters "ATT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| content | RelationshipAttribute |
The actual Content object this LocalAttribute defines the metadata for. |
| createdAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the LocalAttribute was created. |
| succeeds | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing predecessor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. The value of its succeeds property is then the id of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no predecessor, its succeeds property is undefined. |
| succeededBy | string | undefined |
The id of a possibly existing successor of a LocalAttribute. It is possible to update the Attribute contained in the content property of a LocalAttribute using Attribute succession. In this case, a new LocalAttribute, the so-called successor, is created. Its id is then the value of the succeededBy property of the old LocalAttribute, the so-called predecessor. If a LocalAttribute has no successor, its succeededBy property is undefined. |
| wasViewedAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp indicating when the LocalAttribute was firstly viewed. |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity the LocalAttribute was received from. |
| sourceReference | string |
The id of the LocalRequest or LocalNotification the LocalAttribute was received in. |
| initialAttributePeer | string |
This property contains the address of the Identity with whom the emitter has the Relationship in which context the source RelationshipAttribute exists. |
| deletionInfo | ReceivedAttributeDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute is to be deleted or the source RelationshipAttribute is deleted by the emitter, as well as the point in time of that deletion. |
AttributeForwardingDetails
If an Identity has shared an OwnIdentityAttribute with a peer or forwarded an OwnRelationshipAttribute or a PeerRelationshipAttribute to a peer which is not involved in the Relationship in which the RelationshipAttribute exists, AttributeForwardingDetails are created. These help track which peer a LocalAttribute was shared with and when it was shared. This also makes it possible to notify that peer if the LocalAttribute changes.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| attributeId | string |
The id of the LocalAttribute that was shared. |
| peer | string |
The address of the Identity the LocalAttribute was shared with. |
| sourceReference | string |
The id of the LocalRequest or LocalNotification the LocalAttribute was sent with. |
| sharedAt | string |
A timestamp that describes when the corresponding Attribute was shared. |
| deletionInfo | EmittedAttributeDeletionInfo | undefined |
Information about whether the recipient’s Attribute is to be deleted or was deleted by the recipient, as well as the point in time of that deletion. |
AttributeTagCollection
The AttributeTagCollection is defined by the Backbone and specifies which tags are allowed for which IdentityAttribute value.@type.
It can be queried from the Backbone by using the Get AttributeTagCollection use case.
Apart from the Backbone-defined tags, which must start with the prefix bkb:, only tags starting with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$ are allowed to use when working with IdentityAttributes.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| supportedLanguages | string[] |
An array of all supported languages for which a translation must be specified within the displayNames mapping of any AttributeTag within the tagsForAttributeValueTypes mapping. |
| tagsForAttributeValueTypes | Record<string, Record<string, AttributeTag>> |
A mapping of certain IdentityAttribute value.@types and allowed tags. These are represented by a mapping of their names and their specifications as AttributeTags. If an IdentityAttribute value.@type does not occur in the mapping, IdentityAttributes of this value.@type will only be allowed to have tags that start with x: or X:, urn:, language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$, and not with bkb:. |
AttributeTag
AttributeTags occur within the tagsForAttributeValueTypes mapping of the AttributeTagCollection.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| displayNames | Record<string, string> |
A mapping of all supportedLanguages of the associated AttributeTagCollection and the corresponding display names of the AttributeTag. |
| children | Record<string, AttributeTag> | undefined |
A mapping of the names of sub-AttributeTags of the AttributeTag and their specifications. If an AttributeTag has children, the allowed Backbone-defined IdentityAttribute tags will be the concatenation of the prefix bkb: with any concatenation of the name of the AttributeTag itself with the name of any child separated by the tag separator :. |
Content Types
Content Types can be seen as a data contract between Identities. The medium through which this data is exchanged are the Transport types (e.g. Messages, Tokens, …). This chapter shows all the Content types and describes their intended usage.
Request
A Request allows you to ask another Identity to do something.
What this “something” is depends on which of the so called RequestItems were added to the Request (e.g. CreateAttributeRequestItem, ReadAttributeRequestItem, …).
The Request is then sent to the peer via Message or RelationshipTemplate.
The peer can then review the Request and decide whether they want to accept or reject it.
And if they accept it, they can even choose which of the Items they want to accept.
You can also put multiple Items into a RequestItemGroup in order to display them visually as a unit.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | “Request” | |
| id | string | undefined |
Unique identifier of this object. This property is undefined if the Request is inside of a RelationshipTemplate. Remark: the ID of each Request starts with the letters “REQ”. This way you can tell apart a Request ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| title | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable title for the Request. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the Request. |
| expiresAt | string | undefined |
A timestamp that describes when the Request expires on the Backbone. An expired Request cannot be fetched from the Backbone anymore. However, the stored version of the Request on Connector and App will still be accessible. |
| items | (RequestItemGroup | \*RequestItem)[] |
An array of RequestItems and Groups that are part of the Request. There must be at least one Item or Group per Request. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
Optional custom metadata that can be sent together with the Request. This property is meant purely for developers who integrate with enmeshed. They can write for example some kind of key into this property, which can be used later to identify the content of this Request. |
RequestItems
RequestItems can be sent inside of a Request and specify what should be done when the Request is accepted. More information on how to use the individual types of RequestItems for your purposes can be found in the Request and Response introduction. If you are interested in a brief overview of the various operations which can be performed with Attributes, take a look at our Attribute management options.
AuthenticationRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section AuthenticationRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "AuthenticationRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| title | string |
A human readable title for the AuthenticationRequestItem. This title should contain the topic of the authentication. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
ConsentRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section ConsentRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the ConsentRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Request one-time consent of peer guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ConsentRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| consent | string |
The textual consent the user needs to give. This is different to the description of the RequestItem, as the consent would be the actual statement the user agrees to, the description only provides a help text. |
| link | string | undefined |
A valid URL linking to a website which contains more information, like the EULA or privacy terms. |
| linkDisplayText | string | undefined |
If a link is specified, a display text, which is displayed in the App instead of the link’s URL, can be specified for this link. |
| requiresInteraction | boolean | undefined |
If set to true, an explicit action to grant the consent is required, ensuring that it is given intentionally. In case of the enmeshed App, this results in the checkbox associated with the ConsentRequestItem not being preselected and requiring the App user to explicitly tick it. This may be necessary for legal reasons, for example, when the consent involves the processing of sensitive data. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
CreateAttributeRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section CreateAttributeRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the CreateAttributeRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Create Attributes for peer guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "CreateAttributeRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The IdentityAttribute or RelationshipAttribute to create for the peer within the Identity of the peer. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
DeleteAttributeRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section DeleteAttributeRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the DeleteAttributeRequestItem can be found in the Delete Attributes guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "DeleteAttributeRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the emitted Attribute you wish for the peer to delete. This will match the id of the corresponding peer Attribute at the peer’s side. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
FormFieldRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section FormFieldRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction or the Form Fields Within Requests scenario documentation.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "FormFieldRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| settings | BooleanFormFieldSettings | DateFormFieldSettings | DoubleFormFieldSettings | IntegerFormFieldSettings | RatingFormFieldSettings | SelectionFormFieldSettings | StringFormFieldSettings |
The settings that determine the kind of form field. |
| title | string |
A human readable title for the RequestItem. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
BooleanFormFieldSettings
If BooleanFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying a boolean.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"BooleanFormFieldSettings" |
DateFormFieldSettings
If DateFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying a valid date string in ISO 8601 format.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"DateFormFieldSettings" |
DoubleFormFieldSettings
If DoubleFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying a double.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"DoubleFormFieldSettings" |
|
unit |
string | undefined |
Unit of the requested double. |
min |
number | undefined |
Lower limit for the requested double. |
max |
number | undefined |
Upper limit for the requested double. |
IntegerFormFieldSettings
If IntegerFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying an integer.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"IntegerFormFieldSettings" |
|
unit |
string | undefined |
Unit of the requested integer. |
min |
number | undefined |
An integer that serves as the lower limit for the requested integer. |
max |
number | undefined |
An integer that serves as the upper limit for the requested integer. |
RatingFormFieldSettings
If RatingFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying an integer from a lower limit to an upper limit as a rating.
The lower limit for the requested rating is always one, whereas the upper limit can be an integer from five to ten.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"RatingFormFieldSettings" |
|
maxRating |
5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Upper limit for the requested rating. |
SelectionFormFieldSettings
If SelectionFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying a selection of options provided.
If multiple selection is not allowed, the selected option is expected as a string.
Otherwise, a string array of all selected options is expected, which may also contain only one option.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"SelectionFormFieldSettings" |
|
options |
string[] |
Unique options of the selection form field. At least one option must be provided. |
allowMultipleSelection |
true | undefined |
If this flag is set, it will be possible to select multiple of the provided options when responding to the selection form field. Otherwise, exactly one of the options provided must be selected in order to accept the corresponding FormFieldRequestItem. |
StringFormFieldSettings
If StringFormFieldSettings are used as settings of a FormFieldRequestItem, it can be accepted by specifying a string.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
@type |
"StringFormFieldSettings" |
|
allowNewlines |
true | undefined |
If this flag is set, it will be possible to specify a string containing newlines when accepting the corresponding FormFieldRequestItem. |
min |
number | undefined |
A non-negative integer that serves as the lower limit for the length of the requested string. |
max |
number | undefined |
A non-negative integer that serves as the upper limit for the length of the requested string. |
ProposeAttributeRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section ProposeAttributeRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the ProposeAttributeRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Propose Attributes to peer guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ProposeAttributeRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The IdentityAttribute or RelationshipAttribute to propose for the peer as the queried Attribute. |
| query | IdentityAttributeQuery | RelationshipAttributeQuery | IQLQuery |
The structured query of the Attribute the sender would like to receive. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
ReadAttributeRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section ReadAttributeRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the ReadAttributeRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Read Attributes from peer guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ReadAttributeRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| query | IdentityAttributeQuery | RelationshipAttributeQuery | ThirdPartyRelationshipAttributeQuery | IQLQuery |
The structured query of the Attribute the sender would like to receive. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
ShareAttributeRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section ShareAttributeRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the ShareAttributeRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Share Attributes with peer guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ShareAttributeRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The Attribute to be shared can be an IdentityAttribute or a RelationshipAttribute. It is therefore not a LocalAttribute itself, but its content. An overview of the possible kinds of Attributes that can be shared is provided by the table of the combinations and usage scenarios of the ShareAttributeRequestItem. |
| sourceAttributeId | string |
The id of the LocalAttribute which is the source of the shared Attribute. This will be used later to reference the sourceAttribute from its shared copy. |
| initialAttributePeer | string | undefined |
If the Attribute to be shared is a RelationshipAttribute, this property must contain the address of the peer with whom the sender of the Attribute has the Relationship in which context the RelationshipAttribute exists. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
TransferFileOwnershipRequestItem
For more information you should check out the section TransferFileOwnershipRequestItem of the Request and Response introduction. Furthermore, all details on how to use the TransferFileOwnershipRequestItem and examples of use cases for it can be found in the Exchange Files using Attributes guide.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "TransferFileOwnershipRequestItem" |
Specifies the type of the RequestItem for internal processing. |
| fileReference | string |
The value of reference.truncated of the File whose ownership ought to be transferred. |
| ownershipToken | string |
The ownershipToken of the File whose ownership ought to be transferred. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| mustBeAccepted | boolean |
The mandatory mustBeAccepted property is used to differentiate between required and optional RequestItems within the Request.
|
RequestItemGroup
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "RequestItemGroup" |
|
| title | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable title for the RequestItemGroup. |
| description | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable description for the RequestItem. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
The metadata property can be used to provide arbitrary JSON content by the sender of the Request. The metadata is not processed by enmeshed. It is a great way to use your own process descriptors at the time of sending the Request which helps you identify the correct internal process at the time of receiving the Response. |
| items | *RequestItem[] |
The RequestItems inside of this RequestItemGroup. There has to be at least one RequestItem per RequestItemGroup. Note that we do not support nested RequestItemGroups at the moment. If you need this feature, you can raise a feature request. |
Response
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "Response" |
|
| result | "Accepted" | "Rejected" |
Whether the Response was accepted or rejected by the recipient of the Request. |
| requestId | string |
The id of the Request this Response belongs to. The Sender of the Request needs this information to map the Response to the corresponding Request. |
| items | (ResponseItemGroup\|ResponseItem)[] |
An array of Response Items and Groups that are part of the Response. For each RequestItem (Group) of the Request, there must be one Response Item (Group) in the Response. Note that the indices have to be the same for matching Request and Response Items. |
ResponseItems
ResponseItems are sent inside of a Response.
They contain the response data that is sent by the recipient of the Request.
There are three different kinds of ResponseItems: AcceptResponseItem, RejectResponseItem and ErrorResponseItem.
Depending on the actual RequestItem and the DecideRequestItemParameters used, there can be different derivations of these three items.
For more information, please consult the respective chapter of the Request and Response introduction.
AcceptResponseItem
An AcceptResponseItem can be received as answer to an AuthenticationRequestItem or a ConsentRequestItem.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "AcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
AttributeAlreadySharedAcceptResponseItem
An AttributeAlreadySharedAcceptResponseItem can be received as answer to a ReadAttributeRequestItem or ProposeAttributeRequestItem.
It is generated if the Recipient of the RequestItem responds to it with an existing Attribute they already shared with the Sender in case the corresponding AttributeForwardingDetails of the own LocalAttribute don’t have "DeletedByRecipient" as deletionInfo.deletionStatus.
If "ToBeDeletedByRecipient" was previously the deletionInfo.deletionStatus, the deletionInfo will be reset to undefined.
Instead of creating further AttributeForwardingDetails, the id of the already existing shared LocalAttributes is returned.
Note that the id of the own/peer Attribute of the Sender matches the id of the corresponding peer/own Attribute of the Recipient.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "AttributeAlreadySharedAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the already existing shared LocalAttributes. |
AttributeSuccessionAcceptResponseItem
An AttributeSuccessionAcceptResponseItem can be received as answer to a ReadAttributeRequestItem or ProposeAttributeRequestItem.
It is generated if the Recipient of the RequestItem responds to it with an existing Attribute that is a successor of an Attribute they already shared with the Sender in case the corresponding AttributeForwardingDetails of the own LocalAttribute don’t have "DeletedByRecipient" as deletionInfo.deletionStatus.
Instead of creating an independent peer Attribute, internally an Attribute succession is performed.
The id of the already existing shared LocalAttribute predecessor is returned, as well as the id and content of the newly created successor.
Receiving an AttributeSuccessionAcceptResponseItem, the respective shared LocalAttribute of the Sender of the Request is automatically succeeded accordingly.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "AttributeSuccessionAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| predecessorId | string |
The id of the already existing shared LocalAttribute predecessor. |
| successorId | string |
The id of the shared LocalAttribute successor that is newly created. |
| successorContent | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The content of the shared LocalAttribute successor that is newly created. |
CreateAttributeAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "CreateAttributeAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the created LocalAttribute. |
DeleteAttributeAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "DeleteAttributeAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| deletionDate | string |
The timestamp of when the peer will delete the Attribute. |
FormFieldAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "FormFieldAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| response | string | number | boolean | string[] |
The response that is used to fill out the form field. The expected type of response depends on the settings of the FormFieldRequestItem. |
ProposeAttributeAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ProposeAttributeAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the created LocalAttribute. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The IdentityAttribute or RelationshipAttribute to propose for the peer as the queried Attribute. The owner of the Attribute which is proposed can only be the recipient Identity. |
ReadAttributeAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ReadAttributeAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the returned LocalAttribute. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The IdentityAttribute or RelationshipAttribute that will be shared with the peer. |
| initialAttributePeer | string | undefined |
If the Attribute to be shared is an already existing RelationshipAttribute of another Relationship, this property must contain the address of the peer with whom the sender of the Attribute has the Relationship in which context the RelationshipAttribute exists. |
ShareAttributeAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ShareAttributeAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the shared LocalAttribute. |
TransferFileOwnershipAcceptResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "TransferFileOwnershipAcceptResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Accepted" |
The only possible value here is the string "Accepted". |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the returned LocalAttribute. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute |
The IdentityAttribute of type IdentityFileReference that will be shared with the peer. |
RejectResponseItem
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "RejectResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Rejected" |
The only possible value here is the string "Rejected". |
| code | string | undefined |
A code telling the sender about the reason for the rejection. |
| message | string | undefined |
A human readable message with details about the rejection. |
ErrorResponseItem
The ErrorResponseItem is only created by the enmeshed Runtime, in case something happens which hinders you from further processing of the RequestItem.
It will never be created manually.
The properties are:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ErrorResponseItem" |
The type of the ResponseItem. |
| result | "Error" |
The only possible value here is the string "Error". |
| code | string |
An error code telling the sender about the kind of error that occurred. |
| message | string |
A human readable error message with details about the error. |
ResponseItemGroup
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ResponseItemGroup" |
|
| items | ResponseItem[] |
The items inside of this Group. For each RequestItem of the RequestItem Group, there must be one Response Item in the Response Item Group. Note that the indices have to be the same for matching Request and Response Items. |
ResponseWrapper
The ResponseWrapper is a wrapper around the Response that is sent by the recipient of the Request. It contains the Response itself, but also some additional information that is required for the Request to be processed correctly.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ResponseWrapper" |
|
| requestId | string |
The id of the Request this Response belongs to. |
| requestSourceReference | string |
The reference to the Message or RelationshipTemplate the Request was received with. |
| requestSourceType | "Message" | "RelationshipTemplate" |
Specifies if the Request was transferred via Message or RelationshipTemplate. |
| response | Response |
The Response that is sent by the recipient of the Request. |
Notification
Notifications provide you with the possibility to notify a peer about something, e.g. the succession of one of your Attributes. However, unlike Requests they don’t offer the option to make a decision whether or not they want to accept this change. In the example of Attribute succession, the peer can not decide to accept or reject the updated value, but is simply informed about it.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "Notification" |
|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each Notification starts with the letters "NOT". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
| items | NotificationItem[] |
An array of NotificationItems that are part of the Notification. There must be at least one Item per Notification. |
NotificationItems
NotificationItems are sent inside a Notification and specify which processes should be triggered when receiving the Notification.
ForwardedAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem
If an Identity has shared an OwnIdentityAttribute with a peer or forwarded an OwnRelationshipAttribute or a PeerRelationshipAttribute to a peer which is not involved in the Relationship in which the RelationshipAttribute exists, a ForwardedAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem will be sent to the Identity if the peer deletes their forwarded Attribute.
Internally, for the corresponding AttributeForwardingDetails of the Identity’s Attribute, the deletionInfo.deletionStatus will be set to "DeletedByRecipient".
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ForwardedAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem" |
|
| attributeId | string |
The id of the forwarded Attribute that was deleted by the peer. It matches the id of the corresponding Attribute of the Identity. |
OwnAttributeDeletedByOwnerNotificationItem
If an Identity has shared an OwnIdentityAttribute or an OwnRelationshipAttribute with a peer and deletes it, an OwnAttributeDeletedByOwnerNotificationItem will be sent to the peer.
Internally, for the corresponding Attribute of the peer, the deletionInfo.deletionStatus will be set to "DeletedByEmitter" if it wasn’t set to "ToBeDeleted before.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "OwnAttributeDeletedByOwnerNotificationItem" |
|
| attributeId | string |
The id of the own Attribute that was deleted by the owner. It matches the id of the corresponding Attribute of the peer. |
PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem
If an Identity has shared a PeerRelationshipAttribute with a peer and deletes it, a PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem will be sent to the peer.
Internally, for the corresponding OwnRelationshipAttribute or ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute of the peer, the deletionInfo.deletionStatus will be set to "DeletedByRecipient" or "DeletedByEmitter", respectively.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "PeerRelationshipAttributeDeletedByPeerNotificationItem" |
|
| attributeId | string |
The id of the PeerRelationshipAttribute that was deleted by the Identity. It matches the id of the OwnRelationshipAttribute or ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute of the peer. |
PeerAttributeSucceededNotificationItem
A PeerAttributeSucceededNotificationItem will be sent if an Attribute, an Identity has shared with a peer, was succeeded by the Identity and they choose to notify the peer about it. Internally, the succeeded version will then be created at the peer’s side as successor for the previously received Attribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "PeerAttributeSucceededNotificationItem" |
|
| predecessorId | string |
The id of the LocalAttribute that was succeeded. |
| successorId | string |
The id of the LocalAttribute it was succeeded by. |
| successorContent | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The updated content of the LocalAttribute. |
Attributes
An Attribute is some piece of information about an Identity itself (e.g. its name, address, birth date, etc.) or about an Identity in the context of a Relationship (e.g. the customer id the of the user the Relationship). Since the two scenarios differ quite a lot, there are two different types for them: IdentityAttribute and RelationshipAttribute.
IdentityAttribute
IdentityAttributes describe an Identity itself. Their values are strongly normalized. There is a list of available values here.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "IdentityAttribute" |
|
| owner | string |
The Identity that owns this Attribute. Only the owner of an Attribute is allowed to change it after its creation. |
| value | IdentityAttributeValue |
The Attribute’s value. |
| tags | string[] | undefined |
To specify additional information. A tag is valid if it is contained in the AttributeTagCollection and starts with the prefix bkb: or if it starts with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$. |
RelationshipAttribute
RelationshipAttributes describe an Identity in the context of a Relationship.
While there are some types that can be used as a value for a RelationshipAttribute, these types are rather generic (e.g. ProprietaryString, ProprietaryInteger, …).
| Name | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| @type | "RelationshipAttribute" |
||
| owner | string |
The Identity that owns this Attribute. Only the owner of an Attribute is allowed to change it after its creation. | |
| key | string |
An arbitrary key that is set by the creator of this Attribute. It is used to identify the Attribute in a query, especially by a third party. Example: you could set something like customerId in case of a customer id. |
|
| isTechnical | boolean | undefined |
Defines whether the RelationshipAttribute contains data that is actually relevant for the user (isTechnical=false) or whether it should be hidden in the UI (isTechnical=true). |
|
| value | RelationshipAttributeValue |
The Attribute’s value. | |
| confidentiality | "public" | "protected" | "private" |
When this property is set to "private", it means that third parties are not able to query this RelationshipAttribute. It therefore only exists in the Relationship it was created in. If the confidentiality is "protected", third parties can query the RelationshipAttribute, but the App shows a warning saying that you should only share it with someone you trust. If the confidentiality is "public", everybody can query the Attribute, without anything special to happen. |
AttributeQueries
One of the main features of enmeshed is sharing Attributes.
For this, an Identity either proactively sends its Attributes to a peer.
Or, if let’s say a company wants to know the birth date of its customer, it can ask for it.
Depending on the exact use case, the latter can be achieved with one of a bunch of RequestItems, like for example a ReadAttributeRequestItem, or a CreateAttributeRequestItem.
All of them have in common that they define a query property, which contains either an IdentityAttributeQuery or a RelationshipAttributeQuery.
IdentityAttributeQuery
An IdentityAttributeQuery is used to query for IdentityAttributes.
For that, it defines the following properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "IdentityAttributeQuery" |
|
| valueType | string |
The type of value that should be queried, e.g. "StreetAddress", "BirthDate" or "Nationality". |
| tags | string[] | undefined |
To specify additional information. A tag is valid if it is contained in the AttributeTagCollection and starts with the prefix bkb: or if it starts with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$. |
You can only query IdentityAttributes owned by the recipient of the query.
RelationshipAttributeQuery
There are cases in which you want to query some data from your peer that is not an IdentityAttribute.
An example for this is when an electricity provider asks for the electric meter number of a new customer.
Since this information is only relevant in the context of the Relationship, an IdentityAttribute wouldn’t make any sense here.
That’s why you would send a RelationshipAttributeQuery.
Its properties are:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "RelationshipAttributeQuery" |
|
| key | string |
The key of the RelationshipAttribute that should be queried. |
| owner | string |
The owner of the queried RelationshipAttribute. |
| attributeCreationHints | RelationshipAttributeCreationHints |
Contains information about the value that will be created, like the value type or its confidentiality. |
RelationshipAttributeCreationHints
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | string |
A short text describing the purpose of the Attribute that is about to be created. |
| description | string | undefined |
A long text describing the purpose of the Attribute that is about to be created. |
| valueType | string |
The value type of the Attribute to be created (e.g. "ProprietaryInteger", "ProprietaryString", …) |
| confidentiality | "public" |"protected" |"private" |
The confidentiality of the Attribute to be created. See RelationshipAttribute for a more detailed description of confidentialities. |
| valueHints | ValueHints | undefined |
Hints for validating the value, e.g. a regular expression or a min/max length. |
ValueHints
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ValueHints" |
|
| editHelp | string | undefined |
A help text you can use to describe the purpose of the Attribute. |
| min | number | undefined |
In case of a string: the minimum length of the string. In case of an integer: the minimum value. |
| max | number | undefined |
In case of a string: the maximum length of the string. In case of an integer: the maximum value. |
| pattern | string | undefined |
A regular expression that is used to validate the value. Only applicable if the value is a string. |
| values | ValueHintsValue[] | undefined |
An array of allowed values. |
| defaultValue | string | number | boolean | undefined |
The default value that is used if no value is provided. |
| propertyHints | Record<string, ValueHints> | undefined |
A set of Value Hints of all properties. The key is the name of the property and the value a ValueHints object. Only applicable if the value is complex. |
ValueHintsOverride
ValueHintsOverride has the same properties as ValueHints, except that all of them are optional.
This type is used for some RelationshipAttribute values
ValueHintsValue
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | number | boolean |
The actual value. |
| displayName | string |
How the value should be displayed on the UI. |
ThirdPartyRelationshipAttributeQuery
If you want to query RelationshipAttributes the Recipient has in the context of a Relationship with a third party, you can use the ThirdPartyRelationshipAttributeQuery.
An example would be the query for the number of a bonus card managed by another company (like Payback).
A ThirdPartyRelationshipAttributeQuery has the following properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ThirdPartyRelationshipAttributeQuery" |
|
| key | string |
The key of the RelationshipAttribute that should be queried. |
| owner | "recipient" | "thirdParty" | "" |
The owner of the queried RelationshipAttribute. Specify the string "recipient" if the Recipient should be the owner of the queried RelationshipAttribute. Use the string "thirdParty" if any of the third parties specified in the array string thirdParty should be the owner. If both the Recipient and each of the given third parties may be the owner, an empty string "" must be specified. Using this option is useful if the owner of the queried RelationshipAttribute is not known in advance. |
| thirdParty | string[] |
The third parties the RelationshipAttribute should be queried from. An address from this array will match the initialAttributePeer property of a ThirdPartyRelationshipAttribute. |
IQLQuery
If you want to query IdentityAttributes by their content, you can use the IQLQuery which is based on the IQL language, a simple and accessible yet powerful query language for IdentityAttributes.
It allows you to specify conditions the IdentityAttribute must match and which may be chained using binary operations.
Every property of the IdentityAttribute’s content may be queried.
For a full explanation of the IQL syntax, see its dedicated documentation page which also includes an interactive demo for you to try out different queries.
If no IdentityAttribute corresponding to the IQLQuery exists at the peer’s side, you are given the possibility to add attributeCreationHints, suggesting to create an IdentityAttribute which matches a specific valueType and optionally tags.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "IQLQuery" |
|
| queryString | string |
The IQL query string specifying which IdentityAttributes to match. See IQL Syntax for a detailed explanation of the syntax. |
| attributeCreationHints | IQLQueryCreationHints | undefined |
Suggestions for creating a new IdentityAttribute, if the query returns no matches. |
IQLQueryCreationHints
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| valueType | AttributeValues.Identity.TypeName |
The value.@type of the IdentityAttribute, which should be created. |
| tags | string[] | undefined |
The tags for the IdentityAttribute, which should be created. A tag is valid if it is contained in the AttributeTagCollection and starts with the prefix bkb: or if it starts with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$. |
RelationshipTemplateContent
Theoretically you can send any kind of data in a RelationshipTemplate.
However, if your peer uses the enmeshed App, it will only be able to process RelationshipTemplates that contain a RelationshipTemplateContent, which looks like this:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "RelationshipTemplateContent" |
|
| title | string | undefined |
An optional, human readable title that should be rendered in the UI. |
| metadata | object | undefined |
Optional custom metadata that can be sent together with the RelationshipTemplate. This property is meant purely for developers who integrate with enmeshed. They can write for example some kind of key into this property, which can be used later to identify the content of this RelationshipTemplate. |
| onNewRelationship | Request |
The Request that should pop up to the user in case there is no Relationship yet. In this Request you can send Attributes of yourself the user needs to in order to know who’s RelationshipTemplate it is (e.g. company name, address, …), as ask for Attributes of the user you need to know in the Relationship, or send some information you already know about the user, so it can be saved in its wallet (e.g. the customer id). |
| onExistingRelationship | Request | undefined |
The Request that should pop up to the user in case a Relationship already exists. An example usage is a Request with an AuthenticationRequestItem for the sake of two-factor authentication. |
ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent
When communicating with a Connector, you can send any kind of data in a RelationshipTemplate by using the ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent" |
|
| value | unknown |
Feel free to insert whatever you want or need. |
RelationshipCreationContent
Theoretically you can send any kind of data in a Relationship’s creationContent.
However, if the RelationshipTemplate’s content was of type RelationshipTemplateContent, the creationContent must be of type RelationshipCreationContent, containing the Response to the Request contained within the RelationshipTemplateContent’s onNewRelationship property.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "RelationshipCreationContent" |
|
| response | Response |
The Response to the Request that was contained in the RelationshipTemplateContent (in the onNewRelationship property). |
ArbitraryRelationshipCreationContent
When receiving a RelationshipTemplate with an ArbitraryRelationshipTemplateContent as a Connector, any kind of data can be sent as creationContent of a Relationship by using the ArbitraryRelationshipCreationContent.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ArbitraryRelationshipCreationContent" |
|
| value | unknown |
Feel free to insert whatever you want or need. |
A Mail can be sent as the content of a Message. It is comparable with the classic email, so its properties should be familiar.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "Mail" |
|
| to | string[] |
The enmeshed addresses of the main recipients of this Mail without duplicates. Only recipients of the Message may be specified here. |
| cc | string[] | undefined |
The enmeshed addresses without duplicates that should receive a copy of this Mail, additionally to the enmeshed addresses of the main recipients specified in to. Only recipients of the Message which are not main recipients of the Mail can receive a copy of it. |
| subject | string |
The subject of the Mail. |
| body | string |
The body of the Mail. |
ArbitraryMessageContent
When communicating with a Connector, you can send any kind of data in a Message by using the ArbitraryMessageContent.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @type | "ArbitraryMessageContent" |
|
| value | unknown |
Feel free to insert whatever you want or need. |
Consumption
DecideRequestItemParameters
In order to answer a Request, the Response must be formulated appropriately.
As an easier interface to do so various DecideRequestItemParameters are provided.
If you want to reject any RequestItem, you must use the RejectRequestItemParameters.
If you want to accept a RequestItem, however, depending on its kind you might need different parameters.
For example, an AuthenticationRequestItem can be accepted using the AcceptRequestItemParameters, but for a FormFieldRequestItem AcceptFormFieldRequestItemParameters are required.
RejectRequestItemParameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "false" |
The only possible value here is the string “false”. |
| code | string | undefined |
A code telling the sender about the reason for the rejection. |
| message | string | undefined |
A human readable message with details about the rejection. |
AcceptRequestItemParameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
AcceptDeleteAttributeRequestItemParameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| deletionDate | string |
The timestamp of when the Attribute will be deleted. Only dates in the future are allowed here. |
AcceptFormFieldRequestItemParameters
The parameters to accept a FormFieldRequestItem.
The response parameter must have a type that matches the settings of the FormFieldRequestItem.
For example, when using BooleanFormFieldSettings, a response of type boolean must be used.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| response | string | number | boolean | string[] |
The response that is used to fill out the form field. |
AcceptProposeAttributeRequestItemParameters
The parameters to accept a ProposeAttributeRequestItem with an existing Attribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| attributeId | string |
The id of the existing LocalAttribute. |
The parameters to accept a ProposeAttributeRequestItem with a new Attribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| attribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The new Attribute. |
AcceptReadAttributeRequestItemParameters
The parameters to accept a ReadAttributeRequestItem with an existing Attribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| existingAttributeId | string |
The id of the existing LocalAttribute. |
| tags | string[] | undefined |
If additional tags are requested, that the exsiting Attibute doesn’t have, yet, they can be specified using this property. A tag is valid if it is contained in the AttributeTagCollection and starts with the prefix bkb: or if it starts with the custom tag prefix x: or X:, the prefix urn:, the prefix language: followed by a valid ISO 639 language code or the prefix mimetype: followed by a valid MIME type matching the pattern ^[a-z-*]+/[a-z-*]+$. |
The parameters to accept a ReadAttributeRequestItem with a new Attribute.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accept | "true" |
The only possible value here is the string “true”. |
| newAttribute | IdentityAttribute | RelationshipAttribute |
The new Attribute. |
IdentityMetadata
An Integrator of a Connector should be able to store arbitrary auxiliary metadata related to an Identity within the Connector and to manage such IdentityMetadata. The common CRUD operations for handling IdentityMetadata are provided by different use cases. There is the Upsert IdentityMetadata use case for creating and updating IdentityMetadata, as well as the Get IdentityMetadata use case and the Delete IdentityMetadata use case.
| Name | Type | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique identifier of this object. Remark: The ID of each IdentityMetadata starts with the letters "IDM". This way you can tell apart such an ID from any other ID just by looking at the prefix. |
|
| reference | string |
The address of the Identity about which metadata is stored. |
saved only locally |
| key | string | undefined |
An additional identifier to store and distinguish multiple IdentityMetadata for the same Identity. There can be at most one IdentityMetadata per reference and key combination. |
saved only locally |
| value | unknown |
Feel free to insert whatever you want or need. However, it must be compatible with the JSON data types string, number, boolean, object, array and null. |
saved only locally |